Java constructors are the methods which are used to initialize objects. Constructor method has the same name as that of class, they are called or invoked when an object of class is created and can't be called explicitly. Attributes of an object may be available when creating objects if no attribute is available then default constructor is called, also some of the attributes may be known initially. It is optional to write constructor method in a class but due to their utility they are used.
class Programming {
//constructor method
Programming() {
System.out.println("Constructor method called.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Programming object = new Programming(); //creating object
}
}
Output of program:
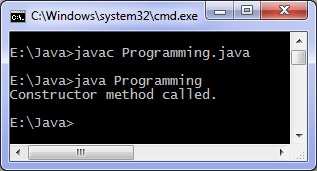
There are three types of constructors:
[button url="http://tekslate.com/tutorials/java-tutorials/" class="other" bg="" hover_bg="" size="0px" color="#eeebeb" radius="0px" width="0px" height="0px" target="_self"] Java Tutorials [/button]
A default constructor is a constructor that either has no parameters, or if it has parameters, all the parameters have default values. If no user-defined constructor exists for a class A and one is needed, the compiler implicitly declares a constructor A::A(). This constructor is an inline public member of its class
Default constructor: If you do not define any constructor in your class, java generates one for you by default. This constructor is known as default constructor. You would not find it in your source code but it would present there. It would look like this if you could see it. Default constructor for class Demo:public Demo() { }no-arg constructor: Constructor with no arguments is known as no-arg constructor. The signature is same as default constructor, however body can have any code unlike default constructor where the body does nothing.
public class MyClass {
private int number = 0;
public MyClass() {
}
public MyClass(int theNumber) {
this.number = theNumber;
}
}
The Java class above contains two constructors. The first constructor is a no-arg constructor, meaning it takes no parameters (no arguments). The second constructor takes an int parameter. Inside the constructor body the int parameter value is assigned to a field, meaning the value of the parameter is copied into the field. The field is thus initialized to the given parameter value. The keyword this in front of the field name (this.number) is not necessary. It just signals to the compiler that it is the field named number that is being referred to. This is explained in more detail in the section about constructor parameters.A constructor doesn’t have a return type.
The name of the constructor must be the same as the name of the class.
Unlike methods, constructors are not considered members of a class.
A constructor is called automatically when a new instance of an object is created.
public ClassName (parameter-list) [throws exception...]
{
statements...
}
The public keyword indicates that other classes can access the constructor. ClassName must be the same as the name of the class that contains the constructor. You code the parameter list the same way that you code it for a method. Notice also that a constructor can throw exceptions if it encounters situations that it can’t recover from. A constructor allows you to provide initial values for class fields when you create the object. Suppose that you have a class named Actor that has fields named firstName and lastName. You can create a constructor for the Actor class:
public Actor(String first, String last)
{
firstName = first;
lastName = last;
}
Then you create an instance of the Actor class by calling this constructor:
Actor a = new Actor("Arnold", " Schwarzenegger");
A new Actor object for Arnold Schwarzenegger is created. Like methods, constructors can be overloaded. In other words, you can provide more than one constructor for a class if each constructor has a unique signature. Here’s another constructor for the Actor class:
public Actor(String first, String last, boolean good)
{
firstName = first;
lastName = last;
goodActor = good;
}
This constructor lets you create an Actor object with information besides the actor’s name:
Actor a = new Actor("Arnold", "Schwarzenegger", false);
If you do not provide a constructor for a class, Java will automatically create a default constructor that has no parameters and doesn’t initialize any fields. This default constructor is called if you specify the new keyword without passing parameters. For example:
Ball b = new Ball();Here, a variable of type Ball is created by using the default constructor for the Ball class. If you explicitly declare any constructors for a class, Java does not create a default constructor for the class. As a result, if you declare a constructor that accepts parameters and still want to have an empty constructor (with no parameters and no body), you must explicitly declare an empty constructor for the class.
You liked the article?
Like: 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.