Are you finding the best sources for your SAP HANA Interview? Then, you’re at the right place. Tekslate experts compiled Top SAP HANA Interview Questions with their descriptive answers. These SAP HANA Interview Questions and answers are best suitable for freshers as well as for the SAP HANA certification exam.
In this article, we will cover the following:
Ans: SAP HANA means High-Performance Analytical Application which is the best tool for database management. It is an in-memory computing engine that encompasses special hardware and software components. It utilizes a real-time information computing/processing engine that gets information legitimately from the in-memory (fundamental memory/RAM) accelerating the information retrieval tasks.
Ans: Following points are advantages of SAP HANA:
Ans: SAP HANA ends up being a unique tool for clients from various perspectives. The purposes behind uniqueness are:
Ans: SAP HANA is an innovation that is an assortment of various techniques and tools that work to get its presence.
There are four advances that on the whole make SAPA HANA:
1. SAP HANA DB: It is the centre in-memory information base that is integral to the working of SAP HANA.
2. SAP HANA Studio: It has a displaying tool for management and data handling.
3. SAP HANA Appliance: It is the Vendor equipment where we introduce SAP HANA programming.
4. SAP HANA Application Cloud: It is a cloud-based foundation guaranteeing the working of appliances.
Ans: SAP HANA supports the following platforms:
| Want to analyze business operations which are based on Big Data, enroll in our " SAP HANA Training" |
Ans: In memory processing, an immense measure of information as the data is put away in the Random-Access Memory (RAM) rather than outside capacity plates. This innovation replaces the conventional method of putting away information on plates and uses social information base administration strategies to bring and deal with the information. In-memory processing innovation is a lot less expensive and quicker than the conventional information-based framework.
Applications in SAP HANA are created in close relationship with the information base and there is nearly no information development required from the data set to the framework. SAP HANA keeps an essential duplicate of the information prepared in-memory stockpiling which brings about information access and handling for specially appointed announcing investigation of information progressively, and snappy question reaction. Likewise, it lessens information intricacy, information repetition, information impression, equipment and IT costs.
Ans: Following are the key components of the SAP HANA:
In-memory processing motor:
This is a segment dwelling inside the Index Server. It has a few sub-parts, for example, Session Management, Planning Engine, Disk Storage, Execution Control, Request Processing, Relational Engine, and so on
Information base:
This component has raw information dwelling in the ERP information base which is shipped off the HANA data set. Replication Agent (in ERP DB) and Replication Server (in the registering motor) arrange this information development. This part gives log-based information provisioning.
SAP Business Objects BI 4:
This part incorporates devices like SBO BI Information Designer apparatus, Data Services Designer, Data Services Server, and Data workers, and so on We utilize the parts for work-based information provisioning. They plan and actualize an occupation on information and store the reports made subsequently. Subsequently, it likewise goes about as a repository.
SAP HANA Studio:
This is a client interfacing stage which is an Eclipse-based tool where we can oversee, regulate, and control information. We can chip away at a few perspectives like Calculation, Attribute, and Analytics.
Clients:
These are random revealing tools that we can associate with the registering motor by using explicit drivers. We can plan and share reports by using these tools and custom applications.
Ans: The replication server is liable for managing the replication of metadata and table data from various data sources.
Ans: The persistence layer is basically responsible for handling information reinforcements intermittently and putting away it for all time. This is known as "Savepoints" and naturally, the savepoint recurrence in every 5 seconds. The information is stored in data volumes and log volumes.
Ans: SAP HANA system contains various components which make a system architecture:
Index server:
The Index Server is the primary worker in SAP HANA. It has the information stockpiling and preparing motor. Inquiries in various dialects like SQL and MDX are gotten in the file worker. At that point, the inquiries are handled by various segments and workers inside it. The record worker additionally deals with the exchanges and confirmations. It likewise has a segment that oversees exchange logs and specifically stores information.
Furthermore, the file worker is additionally isolated into more modest segments like social information motor, meeting chief, approval of executives, arranging motor, calc motor, and tirelessness layer.
Name server:
The name server keeps up the data of the geography or scene of the SAP HANA framework climate. It contains data identified with the name and area of the HANA segments. This worker oversees and screens the geography of the apparent multitude of dispersed workers or hubs. It builds the preparation time by diminishing the re-ordering measure as it keeps the data on what information is stores in which worker.
Pre-processor worker:
A pre-processor worker is a book breaking down the worker who measures printed information. The administration given by this part is utilized during a text search. At whatever point a solicitation starts, this worker measures printed information and gives it to the client.
SAP HANA Studio Repository:
The storehouse stores data identified with the recently delivered refreshes. We can refresh the old adaptation to the most recent ones with the assistance of this.
XS Engine:
It encourages communication between the outside applications (Java and HTML-based) and the SAP HANA framework through HTTP/HTTPS in an internet browser. The XS Engine changes over the framework's state from the persistence stored in the database into the utilization model for customers.
Ans: Following six components in Index Server:
| Checkout Our Blog on SAP HANA Tutorial |
Ans: There are two types of relational data stored in SAP HANA:
Ans: Modeling studio performs multiple tasks in SAP HANA. Following are the multiple tasks that are performed in SAP HANA:
Ans: Following are the three different compression techniques in SAP HANA:
Ans: The transformation rule is the standard determined in the serious replication setting exchange for the source table with the end goal that information is transformed during the replication cycle.
Ans: Following points state the importance of SLT replications in SAP HANA:
Ans: To avoid storing unnecessary data in the SAP HANA database, users need to pause the replication by killing the schema-related jobs in HANA.
Ans: The job is arranged on insistence and it is responsible for the following tasks:
Ans: The logging tables increase when replication is suspended for a long time in the SAP HANA system.
Ans: The transaction chief coordinates database exchanges and tracks running and shut transactions. At the point when the exchange is moved back or submitted, the exchange director advises the included stockpiling motors about the function so they can run vital activities.
Ans: Following are various types of license keys in SAP HANA:
Temporary License keys are mechanically installed when you install the HANA database. These keys are substantial just for 90 days and you should demand lasting permit keys from SAP commercial center before the expiry of this 90 days time span after establishment.
Permanent License keys are substantial till the predefined termination date. Permit keys determine the measure of memory authorized to target the HANA establishment.
Ans: There are two types of permanent license keys in the SAP HANA System:
1. Unenforced
If an unenforced permit key is installed and utilizing the HANA framework surpasses the permit measure of memory, the activity of SAP HANA isn't influenced by this situation.
2. Enforced
If the Enforced permit key is installed and utilizing the HANA framework surpasses the permit measure of memory, the HANA framework gets bolted. On the off chance that this circumstance happens, the HANA framework must be restarted or another permit key ought to be mentioned and introduced.
Ans:
Reinforcement
It is utilized to perform for reinforcement and recuperation in the SAP HANA framework. You can check reinforcement setup subtleties, run manual reinforcement, to check the last effective back performed, and so on for information and log reinforcement.
Index
This contains RDBMS objects like patterns, tables, sees, methodology, and so on You can open SQL manager and plan information base articles
Content
This is utilized to keep up the configuration time archive. You can make new bundles and plan Information sees in the HANA framework. Different perspectives can be made under substance tab to meet the business necessity and to perform systematic reports on the highest point of the Modeling sees.
Provisioning
This is utilized for Smart information admittance to associate with different data sets like HADOOP, TERADATA and SYBASE
Security
This is utilized to characterize clients and to allocate jobs. You can characterize different benefits on various clients utilizing the Security tab. You can dole out Database and Package benefits to various clients to control the information access.
Ans:
Open data preview:
This is used to store the data in a modelling view and object table.
When previewing the data following are the three options:
Open Definition:
It uses the structure of the table, keys, column name, column data types, etc.
Ans: SAP HANA cockpit is an SAP Fiori Launchpad web page that permits you with the solitary purpose of admittance to a scope of Web-based applications for the online organization of SAP HANA. You access the SAP HANA cockpit through a Web program.
To open SAP HANA Cockpit → Right click on HANA system in Studio → Configuration and monitoring → open SAP HANA cockpit
Ans: The catalogue consists of RDBMS objects like views, tables, procedures, schemas, procedures, etc, and also a user can open design database objects and SQL editor.
Content is used to maintain the design-time repository and also you can create new design data views and new packages in the HANA system. Different perspectives can be made under the substance tab to meet the business necessity and to perform investigative reports on the highest point of the modelling views.
Ans: Semantics is defined as a user parameter to define dimensions and measures.
Star Join is used to add other types of views.
The Data Foundation is used to add column base tables.
Ans: Following are various user parameters that define the semantic layer.
Ans: Following are the default nodes that are available in the semantic layer:
Ans: Following are the various modes in data provision in HANA Studio:
Ans: Sizing in SAP HANA refers to governing the hardware prerequisites for explicit SAP HANA establishment necessities. Hardware segments significant for sizing perspective are CPU, memory (RAM) and hard plate. The most vital assignment in measuring is to gauge the size of the worker most appropriate for the business client's prerequisites.
In SAP HANA, the user can perform sizing in the following ways:
Ans: In SAP HANA, the data is stored in the following two ways:
Row Storage is the technique for putting away information in an even manner. It is like how information is put away customarily in circle data sets. In any case, there is one fundamental distinction between the SAP HANA column stockpiling and conventional line stockpiling. That is, in SAP HANA, information is put away in lines in the fundamental memory, and in customary information bases, information is put away in lines in the circle stockpiling.
Column Storage technique stores the information in a columnar manner (direct/vertical). Information is packed effectively in segment stores. It improves SAP HANA's exhibition by upgrading both the peruse and compose procedure on the information. Information is put away in the segment stockpiling region which is separated into two segments; Main stockpiling and Delta Storage.
Ans: SAP HANA studio contains various perspectives which a user can choose to work on them. Following are most used perspectives:
Ans: Utilizing the framework screen in SAP HANA Studio, we can oversee and screen the framework's well-being and accessibility of SAP HANA segments. Additionally, utilizing the framework screen, we can get to the framework's subtleties and setups and the administrations offered by various SAP HANA parts.
We can screen a few perspectives through the SAP HANA framework screen, for example, the alarms, plate space, log circles, follow the circle, information plate, memory, execution, volume, and so forth In this way, it is advantageous to oversee singular viewpoints, errands, and segments.
Ans: Various authoritative tasks can be acted in the SAP HANA Studio, for example, controlling (start/stop) administrations, observing the framework, review strategy, and security design, client the board and approval, reinforcement and recuperation, memory the executives, permit the board, alarms and messages, and so on
The following tasks can be performed from different tabs present in the administration console of SAP HANA Studio:
Ans: Information Modeler explains data perspectives or models on top of the SAP HANA information base utilizing tables in it. Such models are made to serve a business rationale and activity. They are created straightforwardly on top of the HANA information base layer. The data modeller gives the interface and devices to choose ascribes and gauges from the information base tables with the goal that the client can make numerous data sets utilizing the actual tables of value-based information put away in the information bases. The data sees a consistent portrayal of the information which can be additionally distributed or burned through for investigative purposes. Data demonstrating executes on the SAP HANA Modeler viewpoint of SAP HANA Studio.
Ans: The two contrast from one another dependent on track clients. SAP HANA Information Modeler is for specialized clients with broad information displaying prerequisites and specialized information. They can play out a scope of cutting-edge tasks identified with demonstrating, for example, making property sees, logical perspectives, figuring sees, preparing models, information the executives and organization, information stacking and importing/sending out tables.
Though, data arrangers are made for non-specialized clients who are not IT and information science specialists (with no data set or demonstrating information). The data writer has intended to the point that it helps non-specialized clients with easy-to-understand interfaces, movements, clues, and proposals for displaying and announcing.
Ans: Following are three types of information views:
1. Attribute View:
It utilizes credits or the non-quantifiable, non-quantifiable information to configuration perspectives and models as per the business rationale. In this way, the information utilized in quality view is alluded to as 'Ace information' as it is utilized as reference data from different perspectives (expository and figuring). The tables in the trait see don't contain any realities or measure.
2. Analytical view:
We can make star compositions, having a focal exchange or truth table, and various measurement tables connected to it through essential keys. The measures are contained uniquely in the focal exchange table which can be assembled or gotten together with various measurement tables.
3. Calculation view:
It is a serious model that utilizes both quality and investigative view components in it to make a mind-boggling information model after complex business rationale.
It gives us the opportunity to join and make from a scope of alternatives like tables, section sees, investigative perspectives, trait see, and so forth It empowers us to do multidimensional revealing utilizing measures and measurements from various sources.
Ans: SAP Business Objects BI 4 customer instruments are SAP items that offer revealing applications and apparatuses that utilization information from SAP BW and SAP HANA for announcing and investigation reasons. The rundown of detailing and dashboarding devices accessible under SAP Business Objects BI 4 bundle is:
Ans: There are two different ways of making tables in SAP HANA. One strategy is a Command-line technique, where we utilize the SQL comfort to compose SQL content and make a table. The subsequent strategy is a GUI-based technique where we utilize a graphical interface to make a table.
Ans: Following are various connecting drivers that are used by SAP HANA reporting tool:
ODBO (OLE DB for OLAP): The ODBO driver is a driver by Microsoft for interfacing MS Excel to the SAP HANA information base. This driver is explicitly for multi-dimensional announcing (multi-dimensional information stores) and it imparts through MDX language.
ODBC: ODBC represents Open DataBase Connectivity. The ODBC driver is for setting up social information base associations between detailing instruments and SAP HANA information base. Announcing instruments like CR Report and Universe layer (IDE) use an ODBC driver that conveys through SQL.
JDBC: JDBC driver is a Java-based association administration. We likewise use it for social revealing by announcing apparatuses like Explorer, UNX utilizing IDT, CR Report. JDBC drivers speak with the information base through SQL inquiries. JDBC represents Java DataBase Connectivity.
BICS: The BICS driver is SAP legitimacy associating driver. Detailing instruments that utilization SQL DB language as the association language with SAP information base uses BICS driver.
Ans: In the HANA information base, each SQL proclamation is essentially actualized in the reference of the exchange. In this manner in the further cycle, the new meeting is apportioned to another exchange.
Ans:
Real-time: SAP HANA Provides Real-time Data provisioning and Real-time Reporting of information.
Speed: SAP HANA gives elevated level velocities preparing on enormous information and this is expected to In-Memory Technology.
Open to Data/Source: SAP HANA can get to different information sources with no issues including the Structured and Unstructured information from SAP or Non-SAP information source.
Cloud: SAP HANA application and information base can be effectively sent to the Cloud climate.
Simplicity: SAP HANA is most popular for its effortlessness. It additionally decreases the endeavors behind the ETL cycle, Data Aggregation, Indexing, and Mapping.
Cost factor: SAP expresses that SAP HANA Software can diminish the complete IT cost of any organization.
Choice option available: SAP HANA is upheld by the diverse equipment seller and has a rundown of the Software supplier, so dependent on the prerequisite, the client has such a large number of alternatives to can pick the best one.
Ans: Following are various editions of SAP HANA:
SAP HANA Platform Edition:
This stage gives the Core information base innovation. There is an Integration of the SAP segment including the SAP HANA information base, SAP HANA Studio, and SAP HANA customers. It is for clients who as of now have a permit for SAP business objects Data administration and when they need to utilize ETL-based replication.
SAP HANA Enterprise Edition:
This version contains information provisioning (SLT, BODS, DXC) part including center information base innovation. It is just for clients who need to utilize trigger-based replication or ETL-based replication and doesn't have the whole essential permit needed for SAP Business Objects Data Services.
SAP HANA Extended Edition:
This all-inclusive version contains information provisioning the highlights more than some other Platform and Enterprises release. It is the ideal decision for the clients who need to utilize the maximum capacity of all accessible replication situations, even log-based replication.
Ans: The exchange chief coordinates database exchanges and keeps a record of running and shut transactions. When the exchange is moved back or submitted, the exchange supervisor informs the included stockpiling motors about the occasion so they can run essential activities.
Ans: You can maintain a strategic distance from un-vital logging data from being put away by delaying the replication by halting the blueprint-related occupations.
Ans: It is a rule of thumb for deciding whether a data item should be kept in memory, or stored on disk and read back into memory when required. The rule is “randomly accessed disk pages of a cache are re-used every 5 minutes”.
Ans: Waiting for data to be loaded from the main memory into the CPU cache is called Stall.
Ans: The SAP HANA database is developed in C++ and runs on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. It consists of multiple servers and the most important component is the Index Server. It consists of Index Server, Name Server, Statistics Server, Pre-processor Server, and XS Engine.
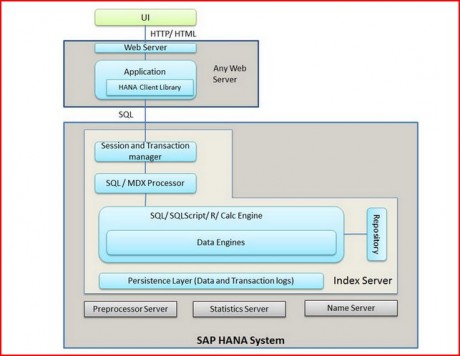
Index Server
Persistence Layer
The database persistence layer is responsible for the durability and atomicity of transactions. It ensures that the database can be restored to the most recent committed state after a restart and that transactions are either completely executed or completely undone.
Preprocessor Server
The index server uses the preprocessor server for analyzing text data and extracting the information on which the text search capabilities are based.
Name Server
It owns the information about the topology of the SAP HANA system. In a distributed system, it knows where the components are running and which data is located on which server.
Statistic Server
The statistics server collects information about status, performance, and resource consumption from the other servers in the system.. The statistics server also provides a history of measurement data for further analysis.
Session and Transaction Manager
The Transaction manager coordinates database transactions and keeps track of running and closed transactions. When a transaction is committed or rolled back, the transaction manager informs the involved storage engines about this event so they can execute the necessary actions.
XS Engine
XS Engine is an optional component. Using XS Engine clients can connect to the SAP HANA database to fetch data via HTTP.
For in-depth knowledge on SAP HANA, click on below
You liked the article?
Like: 1
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.