Welcome to the Weblogic Tutorial. The objective of these tutorials is to provide an in-depth understanding of the Weblogic Application Server.
In addition to free Weblogic Tutorials, we will also cover common interview questions, how-to tutorials and issues and their resolutions of Weblogic Application Server
WebLogic Tutorial - Table of Contents |
Weblogic Server is a sort of server that backings different administrations and in addition find that are connected with JEE applications. WebLogic server is fit for conveying segments and in addition applications through WSDL, UDDI, and SOAP.
A Weblogic server gets designed as a web server by making utilization of HTTP audience for supporting the HTTP. Web servers like that of Apache, Netscape, and Microsoft are utilized. The design of a web server permits WebLogic is fit for giving administrations to dynamic and static demands that are normally produced by servlets, HTML, and JSP.
Weblogic Server is a software product that acts as a liaison between the front end and back end applications. Weblogic Application Server is widely used for its JMS capabilities. Later in these sessions, we will learn in detail about Weblogic Installation, Security, JMS, and Clustering.
The following are the various Weblogic Server versions released from 2o02. The most recent version of Weblogic is 12c.
WebLogic Server 12c Release 3 (12.1.3) - June 26, 2014
WebLogic Server 12c Release 2 (12.1.2) - July 11, 2013
WebLogic Server 12c Release 1 (12.1.1) - Dec 1, 2011
WebLogic Server 11gR1 PS5 (10.3.6) - February 26, 2012
WebLogic Server 11gR1 PS4 (10.3.5) - May 16, 2011
WebLogic Server 11gR1 PS3 (10.3.4) - January 15, 2011
WebLogic Server 11gR1 PS2 (10.3.3) - April 2010
WebLogic Server 11gR1 PS1 (10.3.2) - Nov 2009
WebLogic Server 11g (10.3.1) - Jul 2009
WebLogic Server 10.3 - Aug 2008
WebLogic Server 10.0 - Mar 2007
WebLogic Server 9.2
WebLogic Server 9.1
WebLogic Server 9.0 - Nov 2006
WebLogic Server 8.1 - Jul 2003
WebLogic Server 7.0 - Jun 2002
| Want to acquire industry skills and gain complete knowledge of WebLogic? Enrol in Instructor-Led live WebLogic Training to get Job Ready! |
WebLogic server is based on Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition (J2EE), the standard platform used to create Java-based multi-tier enterprise applications. J2EE platform technologies were developed through the efforts of BEA Systems and other vendors in collaboration with the main developer, Sun Microsystems.
Oracle WebLogic Server supports Oracle, DB2, MS SQL Server, MySQL Enterprise, and other JDBC-compliant databases. Oracle Weblogic Platform also includes:
Standards Supported by version
The table below lists major standards supported by the WebLogic Server product version.
| Standard | WLS 7.0 | WLS 8.1 | WLS 9.0 | WLS 10.0 | WLS 10.3 |
| Java | 1.3 | 1.4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| Java EE | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 5 | 5 |
System administration of WebLogic Server includes a wide range of tasks: creating WebLogic Server domains; deploying applications; migrating domains from development environments to production environments; monitoring and managing the performance of the run-time system; diagnosing and troubleshooting problems. (A WebLogic Server domain is a collection of WebLogic Server services designed for a specific purpose. For example, you might create one domain to provide an employee portal and another domain to provide business services to your customers.)
Because the WebLogic Server management system is based on Java EE and other standards, it integrates with systems that are frequently used to manage other software and hardware components. In addition, WebLogic Server includes several of its own standards-based, extensible utilities. Alternatively, you can use APIs to create custom management utilities.
At the end of this module you will be able to:
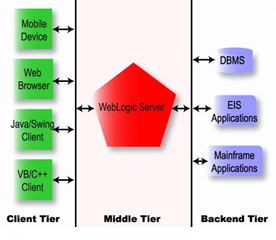
The software components of a multitier architecture consist of three tiers:
| Checkout Our Blog on WebLogic JDBC |
A Web server handles the HTTP protocol. When the Web server receives an HTTP request, it responds with an HTTP response, such as sending back an HTML page. To process a request, a Web server may respond with a static HTML page or image, send a redirect, or delegate the dynamic response generation to some other program such as CGI scripts, JSPs (JavaServer Pages), servlets, ASPs (Active Server Pages), server-side JavaScripts, or some other server-side technology. Whatever their purpose, such server-side programs generate a response, most often in HTML, for viewing in a Web browser.
Understand that a Web server's delegation model is fairly simple. When a request comes into the Web server, the Web server simply passes the request to the program best able to handle it. The Web server doesn't provide any functionality beyond simply providing an environment in which the server-side program can execute and pass back the generated responses. The server-side program usually provides for itself such functions as transaction processing, database connectivity, and messaging.
While a Web server may not itself support transactions or database connection pooling, it may employ various strategies for fault tolerance and scalability such as load balancing, caching, and clustering—features oftentimes erroneously assigned as features reserved only for application servers.
Proxy some requests to Application Servers

As for the application server, according to our definition, an application server exposes business logic to client applications through various protocols, possibly including HTTP. While a Web server mainly deals with sending HTML for display in a Web browser, an application server provides access to business logic for use by client application programs. The application program can use this logic just as it would call a method on an object (or a function in the procedural world).
Such application server clients can include GUIs (graphical user interface) running on a PC, a Web server, or even other application servers. The information travelling back and forth between an application server and its client is not restricted to simple display markup. Instead, the information is program logic. Since the logic takes the form of data and method calls and not static HTML, the client can employ the exposed business logic however it wants.
In most cases, the server exposes this business logic through a component API, such as the EJB (Enterprise JavaBean) component model found on J2EE (Java 2 Platform, Enterprise Edition) application servers. Moreover, the application server manages its own resources. Such gate-keeping duties include security, transaction processing, resource pooling, and messaging. Like a Web server, an application server may also employ various scalability and fault-tolerance techniques.

Application servers:
Checkout: [ WebLogic Server Installation ]
Application Server: A server that exposes business logic to client applications through various protocols including HTTP.
Web Server: A server that handles HTTP protocol.
Application Server: To deliver various applications to another device, it allows everyone in the network to run software off of the same machine.
Web Server: Keeping HTML, PHP, ASP, etc files available for the web browsers to view when a user accesses the site on the web, handles HTTP requests from clients.
Application Server: GUI’s, Web Servers
Web Server: HTTP, HTML
Application Server: Adds functionality
Web Server: Does not add any
Application Server: Oracle OC4J(Oracle), Sybase Application server(Sybase), SAP Netweaver (SAP), JBoss (Red Hat), Weblogic server (Oracle), WebSphere (IBM)
Web Server: Microsoft IIS, Apache Tomcat
| Checkout Our Blog on Work Managers in WebLogic |
WebLogic Server J2EE applications are based on standardized, modular components. WebLogic Server provides a complete set of services for those modules and handles many details of application behavior automatically, without requiring programming.
J2EE includes deployment specifications for Web applications, EJB modules, Enterprise applications, client applications, and connectors. J2EE does not specify how an application is deployed on the target server—only how a standard module or application is packaged.
Java is platform-independent, so you can edit and compile code on any platform, and test your applications on development WebLogic Servers running on other platforms. For example, it is common to develop WebLogic Server applications on a PC running Windows or Linux, regardless of the platform where the application is ultimately deployed.
Weblogic Tutorial Summary:
Our course design of tutorials is practical and informative. At TekSlate, we offer resources to help you learn various IT courses. We avail of both written material and demo video tutorials. For in-depth knowledge and practical experience explore Online WebLogic Training.
You liked the article?
Like: 1
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.