All tables, procedures, generals, indexes, sub tables, etc Required permanent memory
Views, Macro, and Trigger doesn’t require any permanent memory
A database can be created without permanent memory]
i) It stores intermediates result and calculation(Select statement result, join operation data, etc)
ii) View, macros, derived tables, etc, store under spool memory
i) It holds intermediate result and calculation[generally session-level information]
ii)global temporary tables store under temporary memory
Note- The un-used permanent can be taken as spool(or) temper are memory
There is a database with 100GB of memory, 60 GB Assign to spool, 40GB Assign to permanent, 20 GB OF Permanent data stored, How much spool memory available for business operations.
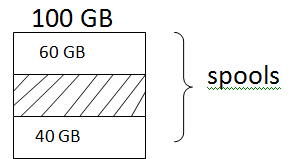
Spools = Assigned spool+ un- used permanent
=60+20
=80GB
Inclined to build a profession as Teradata Developer? Then here is the blog post on, explore Teradata Training
Currently, occupied memory is the current memory
The maximum occupied of memory earlier is peak memory
Max memory assigned(earlier maximum memory) to the object.
1)A database is a passive repository where it stores all database objects
2) Until you create an object, it is empty
3)Database doesn’t contain any passwords
Example:
create database<database name>FROM
<Parent database>
As
Permanent=<Memory space>,
Spool=< Memory space >,
Temporary=< Memory space >,
[No]FALL BACK
Before/After journal,
Default journal table=<DATABASE.TABLE NAME>;//FOR
Permanent journal.
Syn: DROP database<database/USER>;
EG:DROP database MEERA;
Modifying database/user<database/USER;>
PERMANENT/Spool/TEMPORARY=<MEMORY SPACE>
Example:
Create database db-DEVELOPMENT
From DBC
AS
PERMANENT=2000000,
Spool=2000000,
TEMPORARY=2000000,
![]() SELECT*FROM DBC.databaseS
SELECT*FROM DBC.databaseS
![]() CREATE TABLE DB- DEVELOPMENT. TEST[PARTY ID INTEGER, PARTY NAME VARCHAR(30)]
CREATE TABLE DB- DEVELOPMENT. TEST[PARTY ID INTEGER, PARTY NAME VARCHAR(30)]
![]() INSERT INTO DB- DEVELOPMENT.TEST(1,’Meera’)
INSERT INTO DB- DEVELOPMENT.TEST(1,’Meera’)
![]() Select *FROM DB- DEVELOPMENT.TEST
Select *FROM DB- DEVELOPMENT.TEST
A user inactivates the repository (data dictionary), where it stores all database objects.
Until you create an object, the user is an empty
User contains a password whereas the database doesn’t contain any Password
![]() Create USER- DEVELOPMENT
Create USER- DEVELOPMENT
FROM DBC
AS
PERMANENT=2000000,
Spool =2000000,
TEMPORARY=2000000,
PASSWORD= VINAY;
![]() Select * FROM DBC.USERS
Select * FROM DBC.USERS
![]() Create a table user- DEVELOPMENT. Test(Party ID Integer, party name varchar(30))
Create a table user- DEVELOPMENT. Test(Party ID Integer, party name varchar(30))
![]() Insert INTO USR – DEVELOPMENT.TEST(‘VINAY’)
Insert INTO USR – DEVELOPMENT.TEST(‘VINAY’)
![]() SEL* FROM USE- DEVELOPMENT. Test
SEL* FROM USE- DEVELOPMENT. Test
| database | USER |
| 1.Passive repository[NO Change in request resource] | 1.Active repository[changes in the number of request and responses] |
| 2.Doesnot contain the password | 2.Contain password |
| 3.To work with database we require user support | 3.By using this we can do any tool in tera data. |
Note:-
In real-time for individual number(or) group administrator create
user id and password.
Creating an ODBC DRIVER with the above user
Open data sources



Now we are in the above userspace
![]() Connecting other databases (or)use They are 2 ways
Connecting other databases (or)use They are 2 ways
By prefixing database name(or)USER name before the object
Syn:-<database/user name><object name>
Example:- SQL*FROM VINAYAKA. PARTY
database Table
By takes database name(or)User name as a current database name[Multiple queries we can execute without prefixing database(or)user name]
Syn:-<database/ database /USER name>
Example:- Database VINAYAKA;
Select *From party;
Select *From party;
Select *From VIEW-party;
You liked the article?
Like: 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.