Data Recovery And Protection in Teradata

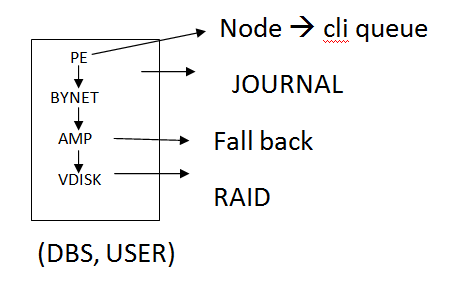
Locks:- Prevent simultaneous access to the objects
RAID:- Prevent from disk failure
Fall back:- Prevent from Amp failure
Journal:- Prevent from Image failure
CLIQUE:- Prevent from Node failure
ARC[Archive and Recovery]
A Means of Archiving data to tape and disk and restoring data to teradata database backup application software includes the following
Teradata archive and recovery, Net Valet, Net Backup, Tivoli Storage Manager, Teradata Extension.
Note:- the above all feature are provides teradata, to makes teradata as highly

|
LOCK Held |
Table Name |
“A” having Lock Access |
Read |
Write |
Exclusive |
|
Access |
√ | √ | √ | √ |
X |
|
Read |
√ | √ | √ |
X |
X |
|
Write |
√ | √ |
X |
X |
X |
|
Exclusive |
√ |
X |
X |
X |
X |
Inclined to build a profession as Teradata Developer? Then here is the blog post on, explore Teradata Training
Access
DATA Inconsistent, select
Read
DATA consistent, select
Write
Insert, Update, Delete
Exclusive
DDL Statement
HUT LOCK
- This is the lock applied while we are doing archive and recovery.
Syntax- Locking row for
<Lock type><Sql Queue >
Example
Locking row for access SEL* From party Locking row for write SEL*from party
Syntax Table level
Locking table<Table name> for
<Lock type>
Example Locking table party for access
Release Lock
Syn Release Lock database name Table name:
Advantages of Access Lock
a) Permit queue access to a table multiuser Environment
b) Having minimal blocking efforts on other queries
c) Very use full for aggregating a huge number of rows.
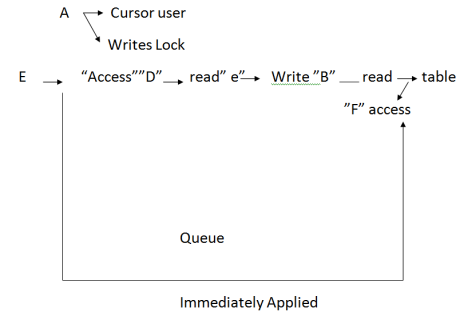
![]() Access Lock applied Immediately even though there are many locking it’s that query
Access Lock applied Immediately even though there are many locking it’s that query
Note- Refer to the complete description And practical page NO:50 to 52 new material
RAID-[REDUNDENT ARRAY OF INDEPENDENT DISK DRIVE] Refer to the page No: 53 To 54 for the description
RAIDO,RAID1,RAID2,------RAID5,RAIDS,RAIDE etc.,
Teradata supports
RAID1, RAID5, RAIDS
RAID1:[MIRRORING TECHNIQUE] Real-time use
Advantage:-quick Availability, primary disk failure, recovers a/s easier

Drawback
- 50% Memory wastage
- Operations double[Insert, update, Delete]
RAID5:-[PARTY CHECKING TECHNIQUE]

P= B1+B2+B3
B1=P- B2-B3
Advantage 25% only memory addition[less memory]
Drawback: Recovery slow
Fall back:- Refer to the page no:54
Usage: At the time of AMP failure, it permits to access rows in others AMP’S
Party: PID PNM
1 X
2 Y
3 Z
4 M

Advantage: High availability or fast data[At time of failure, immediate redirection to fall back AMP, so that data highly accessible]
Drawback
- 50% Space waste
- Operations double
Note: In real-time we use raid1 and fall back as part of data protection and recovery general we back cluster environment in real-time
Fall back Cluster(3,4,8,16)
Usage: Cluster is nothing but a group of Amp’s, then it takes a single place, where fall back maintain with in the same group
It is an advantage because we will skip scanning other Amp’s And other groups
Note: If 2 Amp’s went down RDBMS halted, Tera data recommend 4 Amp’s for the cluster for detail description refer to page No:55 To get average performance
Journal: Journal is a kind of record, which close some kind of activity
| No. of Amp(N) | Workload1+1/N-1 | Remains should available |
| 16 | 1.06 | 15 |
| 8 | 1012 | 7 |
| 4 | 1.3 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 |
Journal Types
- Recovery journal
- Transient Journal
- Permanent journal
Single image ![]() one copy of data
one copy of data
Dual image ![]() two copies of the data
two copies of the data
Before image![]() before the change
before the change
Afterimage ![]() after change taking the image
after change taking the image
Recovery Journal
- Automatic[of fall back is there]

Usage Once the down Amp came online[repaired] to recovery successfully, recovery journal log are useful
2.Transcient journal
[it helps is to do successful]
- Transaction nothing but a logical collection of the statement, which can be either failure or successful
- Here transaction journal helps to do a successful roll back in case of transaction failed.
Successful Transaction Failed Transaction
BEGIN Transaction;//;Transient _________________ journal activated(T.J)
- S) INSERT PARTY;//Back up image ____________ B.I (B.I)taken
- S) UPDATE PARTY; ________(party)
- S) Delete Party; ________(failed)
END TRANSACTION;
1.Drops B. I B. I dropped 1.Roll back happens
2.Discards T.J T.J discarded 2.B.I replied
Note: Transient journal uses before image for its operations
3.Permanent journal
- It helps us to do fall(or)partial selective recovery
- It uses both before and after image[single and clual]
Ex: Till yesterday the data was corrupted
Till yesterday ![]() B.I
B.I
Mon à A.I
|
|
|
Sun ![]() A.I
A.I
Full recovery= B.I+[Mon-Sun] A.I
Selection recovery = B.I+[Mon-This] A.I
Note:- Refer to the material description of example the material
CheckSum
- It used to prevent disk input, output Errors
- A checksum is completed value, from in algorithm generated by an algorithm on the data block this Algorithm applied storage and retrieval level it these are no difference, there a no disk input, output error

If x=y No, disk input, output error
If x<>y, disk input, output error
Default:- Algorithm applied on data block recording value specified DBC Control utility according to table type
Note:- Many people they using in real-time to implement Change data capturing concepts
Clique:-
- Group of nodes sharing common disk array Driver is called clique
- Each and every multi-system have at least one clique
- The nodes of clique connected to the controls of the disk array
- Each clique has the same no of nodes
Advantages:-
- It provides data availability, even the nodes failed by Migrating virtual processor[PE, AMP]
- Migrating from fail node other nodes [operation node]
Note:-
- Multiple cliques in the same system must have the same no. of nodes
- All these nodes communicate with each other by using by NET
HSN[HOT STAND BY NODE]
It is a node, that is a number of cliques that do not configure that execute any tera data vproc if a node in the clique fail
The Amps from the fail node move to the thigh HSN Stand by Node in this way it decreases performance in Zero space zero percentage
You liked the article?
Like : 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium
Recommended Courses
1/6
About Author

Name
TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.
Stay Updated
Get stories of change makers and innovators from the startup ecosystem in your inbox